从setContentView()开始
1 |
|
1.当我们在Activity的onCreate的setContentView()方法中直接写入布局的ID,来看看这中间经历了什么从而加载到了我们的手机屏幕上。
1 | Activity中 |
generateDecor()
1 | protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) { |
1.方法比较简单,只是对dectorview进行了实例化操作,没有特别需要主要的点。
generateLayout()
1 | ----省略---- |
1.layoutResource:定义了一个资源布局,根据不同的主题,加载了不同layout资源文件,当然这属于系统内部的layout,也就是基础容器,不同的theme加载的layout是不同的。而我们还需要的关心的是,我们在设置setContentView(R.layout.xxxx)是如何被加载到屏幕上的。
2.在看ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);之前,注意mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);这个方法,对于基础容器decorview的一系列初始化完成之后,是通过addview,在基础容器创建了一个viewgroup,以便后续将我们自身的布局加载到这个viewgroup中。1
2
3
4
5/**
* The ID that the main layout in the XML layout file should have.
*/
//源码解释的很清楚,我们自身的layout资源id映射到系统的对应参数上。
public static final int ID_ANDROID_CONTENT = com.android.internal.R.id.content;
3.以上即view被加载到窗口上的主要过程,主要关系图: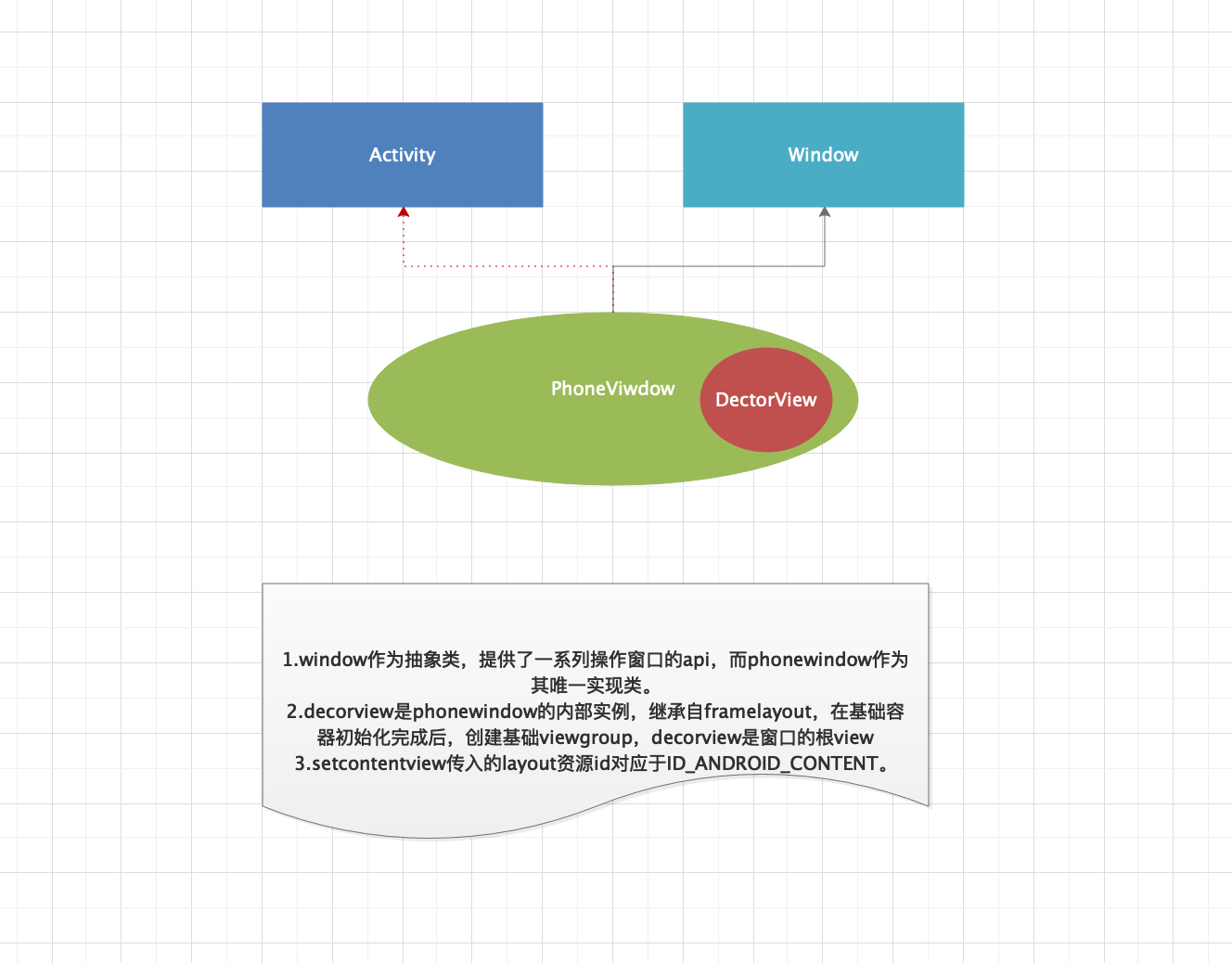
4.视图层级关系图: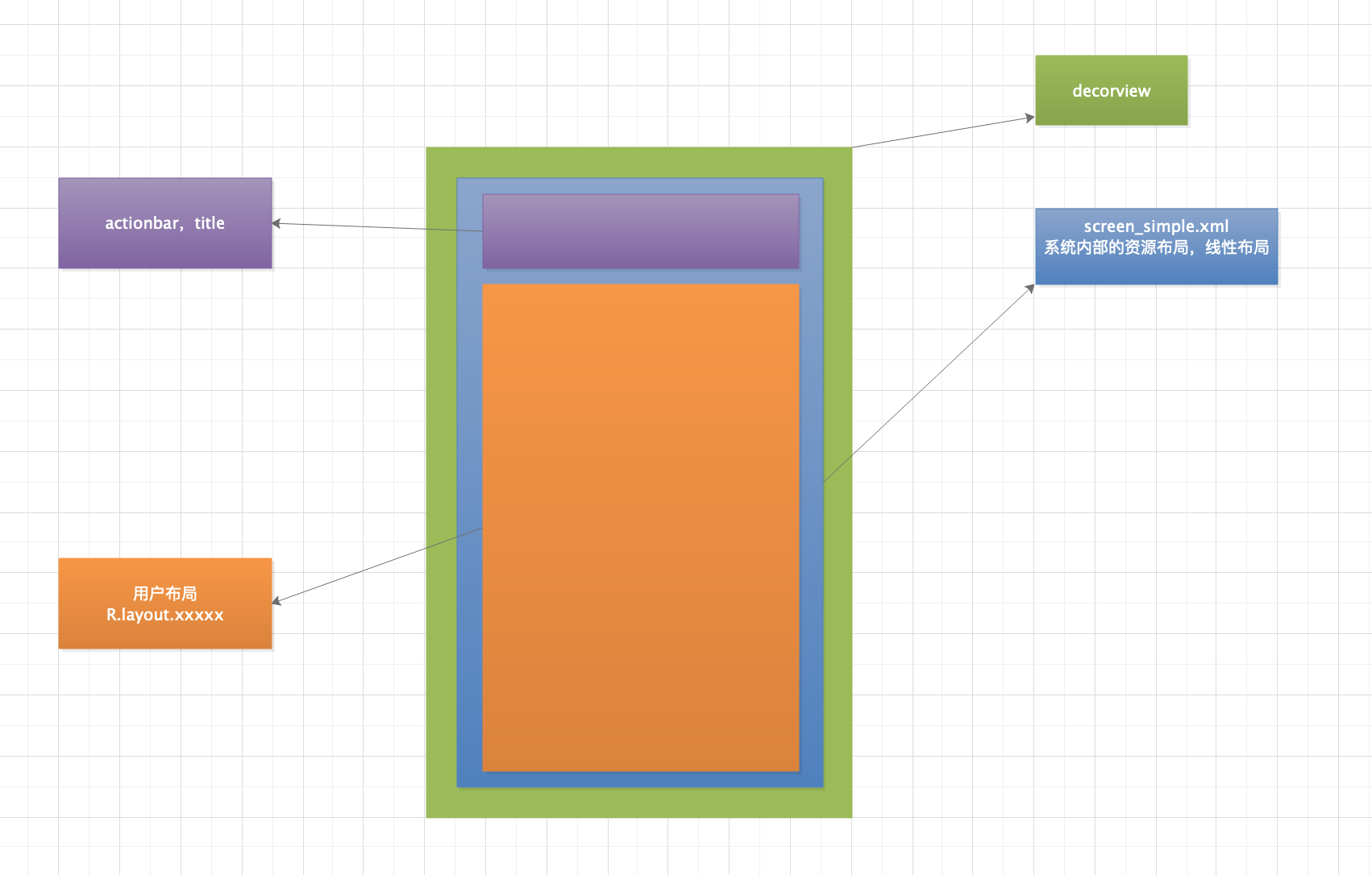
ViewRootImpl
1.在ActivityThread中,熟悉源码就会知道,handleResumeActivity是作为绘制的主入口。Window作为ViewRootImpl与Activity之间的桥梁起到了关键的作用。先看主要流程。
handleResumeActivity
1.wm.addView(decor, l); l = LayoutParams,windowManager通过addView将decor与LayoutParams参数关联。而WindowManagerImpl继承自WindowManager:1
2
3
4
5
6
7WindowManagerImpl中
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
}
mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal
2.WindowManagerGlobal的addview中对ViewRootImpl作了初始化:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18.....
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
//setView中关键方法requestlayout,就是我们所熟悉的主线程的检查,和scheduleTraversals(),这是进入绘制流程的前期准备工作。
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
scheduleTraversals()
1 | void scheduleTraversals() { |
小结
1 | 1.经过分析得出,View绘制的前期工作流程很清晰: |
1 | 2.进一步划分,绘制入口: |
measure()
1 | ViewRootImpl |
先看MeasureSpec源码中解释:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85/*
* MeasureSpecs are implemented as ints to reduce object allocation. This class
* is provided to pack and unpack the <size, mode> tuple into the int.
*/
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/** @hide */
({UNSPECIFIED, EXACTLY, AT_MOST})
(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public MeasureSpecMode {}
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint
* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.
*/
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size
* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless
* of how big it wants to be.
*/
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up
* to the specified size.
*/
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size,
@MeasureSpecMode int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
public static int makeSafeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec && mode == UNSPECIFIED) {
return 0;
}
return makeMeasureSpec(size, mode);
}
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
//noinspection ResourceType
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
static int adjust(int measureSpec, int delta) {
final int mode = getMode(measureSpec);
int size = getSize(measureSpec);
if (mode == UNSPECIFIED) {
// No need to adjust size for UNSPECIFIED mode.
return makeMeasureSpec(size, UNSPECIFIED);
}
size += delta;
if (size < 0) {
Log.e(VIEW_LOG_TAG, "MeasureSpec.adjust: new size would be negative! (" + size +
") spec: " + toString(measureSpec) + " delta: " + delta);
size = 0;
}
return makeMeasureSpec(size, mode);
}
public static String toString(int measureSpec) {
int mode = getMode(measureSpec);
int size = getSize(measureSpec);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("MeasureSpec: ");
if (mode == UNSPECIFIED)
sb.append("UNSPECIFIED ");
else if (mode == EXACTLY)
sb.append("EXACTLY ");
else if (mode == AT_MOST)
sb.append("AT_MOST ");
else
sb.append(mode).append(" ");
sb.append(size);
return sb.toString();
}
}
1.MeasureSpec定义了三种模式UNSPECIFIED、EXACTLY、EXACTLY,也就是我们平时使用的WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT、dp、px,将mode与size打包保存在MeasureSpec中。由于int有32位,取前两位作为mode,而后30位作为size。
2.Framelayout中的onMeasure方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//容器类的view测量,都需要层层遍历子view
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
//测量子view后的最大宽高,包含了margin的值,padding,以及子view是否设置的最小宽高
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
//测量子控件完成后,决定自身的宽高(ViewGroup),并保存
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
//走到这里还是调用measure方法,也即递归操作,对于子view如果是viewgroup还是走一遍以上的逻辑,直到全部测量完成,在我们实际开发过程中,可想而知如果view的层级过深,是不利于性能的。因为测量是一个递归遍历操作。
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
View中:
/**
* <p>This method must be called by {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} to store the
* measured width and measured height. Failing to do so will trigger an
* exception at measurement time.</p>
*
* @param measuredWidth The measured width of this view. May be a complex
* bit mask as defined by {@link #MEASURED_SIZE_MASK} and
* {@link #MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL}.
* @param measuredHeight The measured height of this view. May be a complex
* bit mask as defined by {@link #MEASURED_SIZE_MASK} and
* {@link #MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL}.
*/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
////当我们自定义view时,可见如果不在onmeasure重写,决定自己的宽高,那么设置matchparent与wrapcontent效果是一样的。
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
layout()
1 | //确定了自身的上下左右的位置 |
1 | 1.view的布局比较简单,调用view.layout(),确定left、right、top、bottom的值,也即确定自身的位置。 |
draw()
1 | 绘制方法相对比较简单 |

